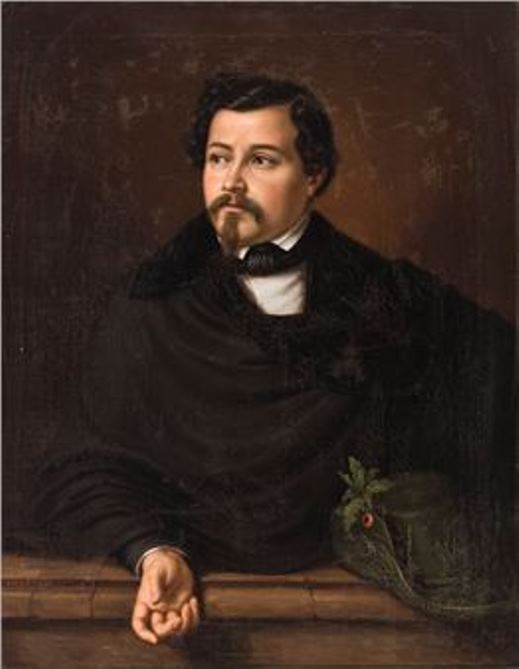
richard pare


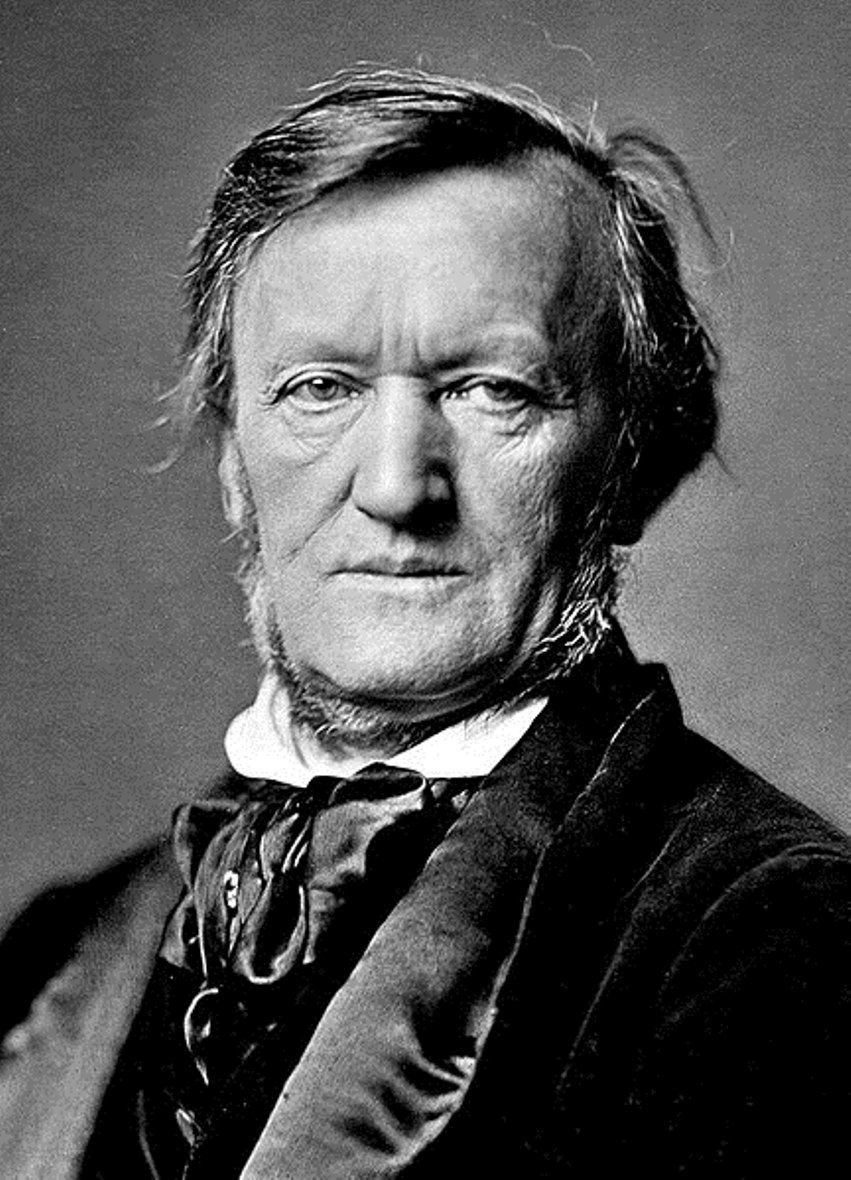
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).
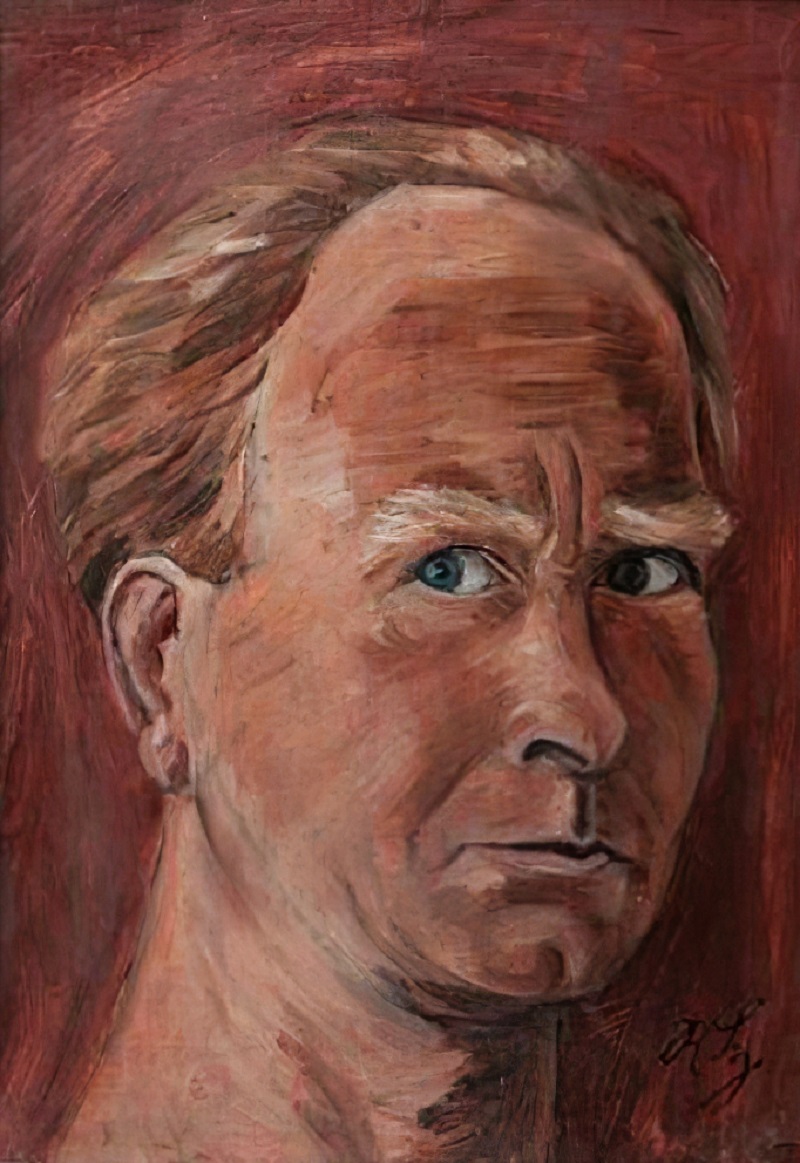


Richard Haizmann was a German painter, sculptor, ceramist and woodcutter.

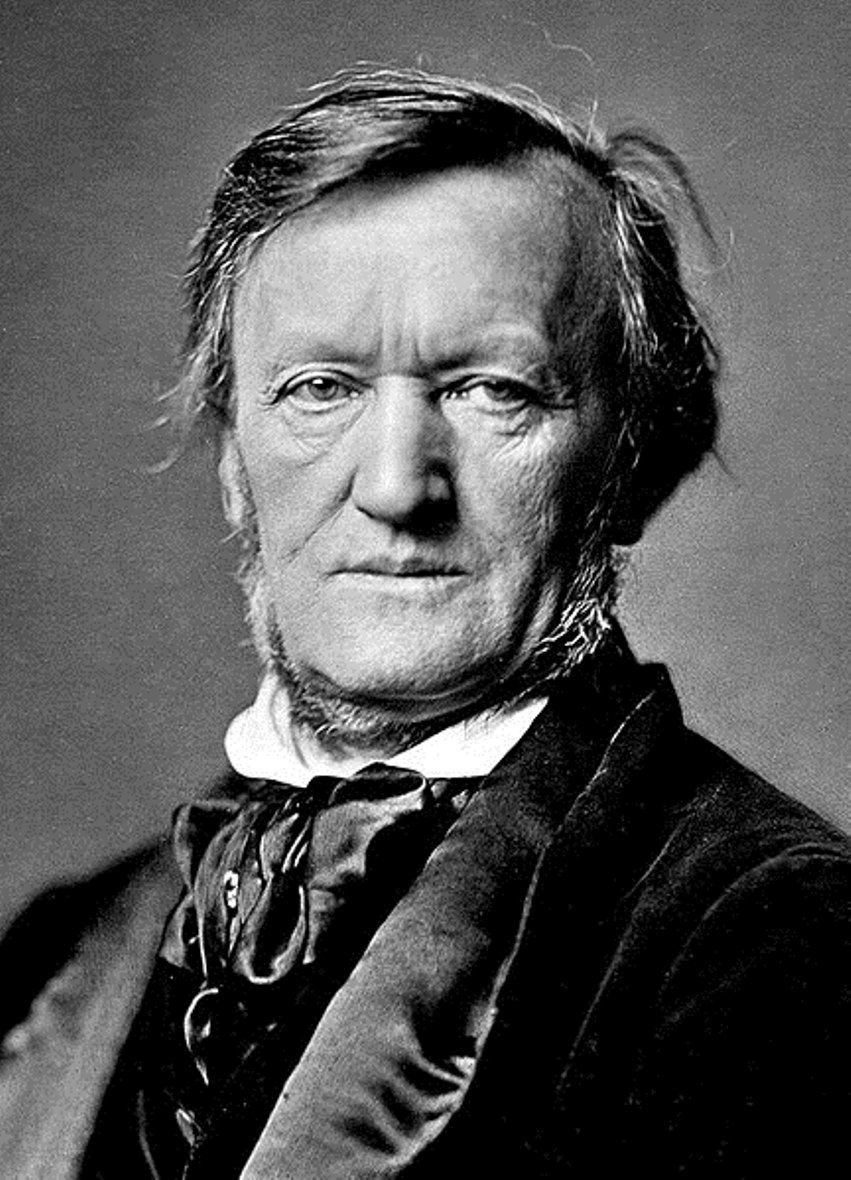
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).

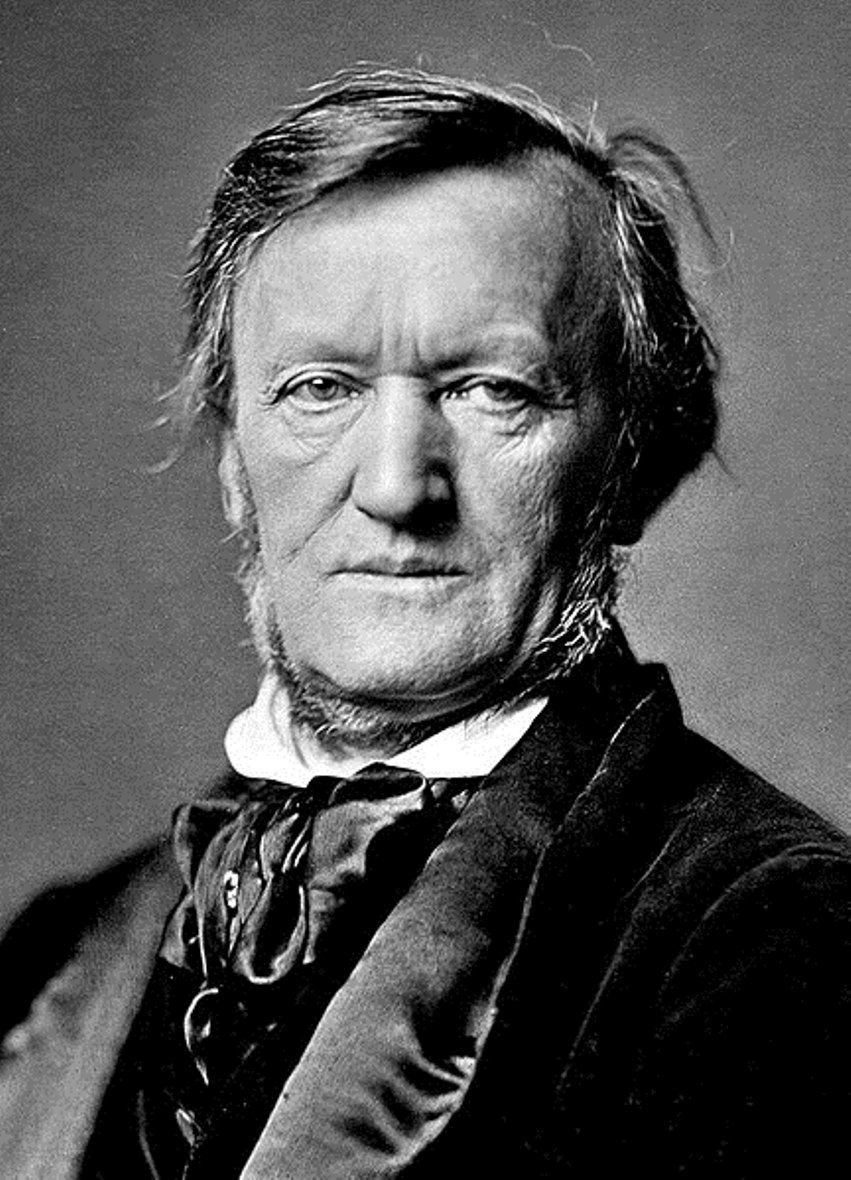
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).


Richard Wilson was an influential Welsh landscape painter, who worked in Britain and Italy. With George Lambert he is recognised as a pioneer in British art of landscape for its own sake and was described in the Welsh Academy Encyclopedia of Wales as the "most distinguished painter Wales has ever produced and the first to appreciate the aesthetic possibilities of his country". In December 1768 Wilson became one of the founder-members of the Royal Academy. A catalogue raisonné of the artist's work compiled by Paul Spencer-Longhurst is published by the Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art.

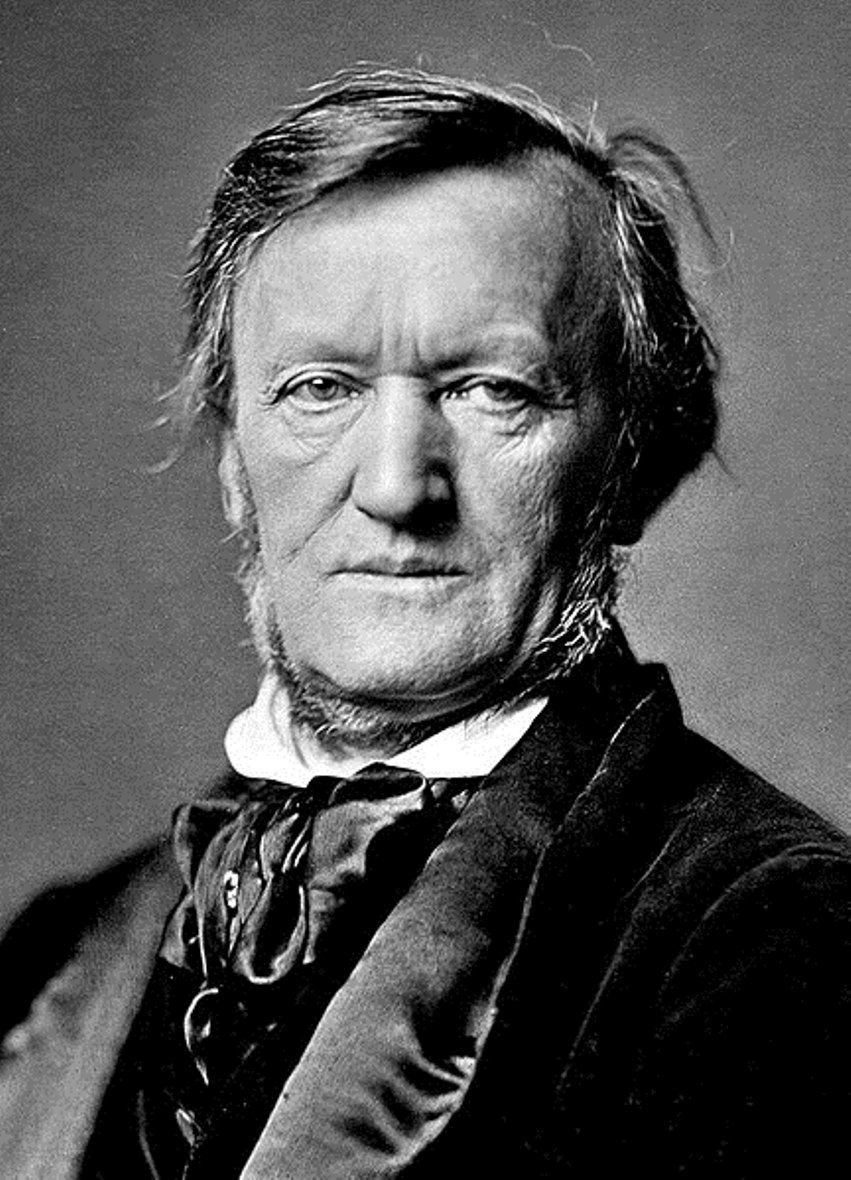
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).

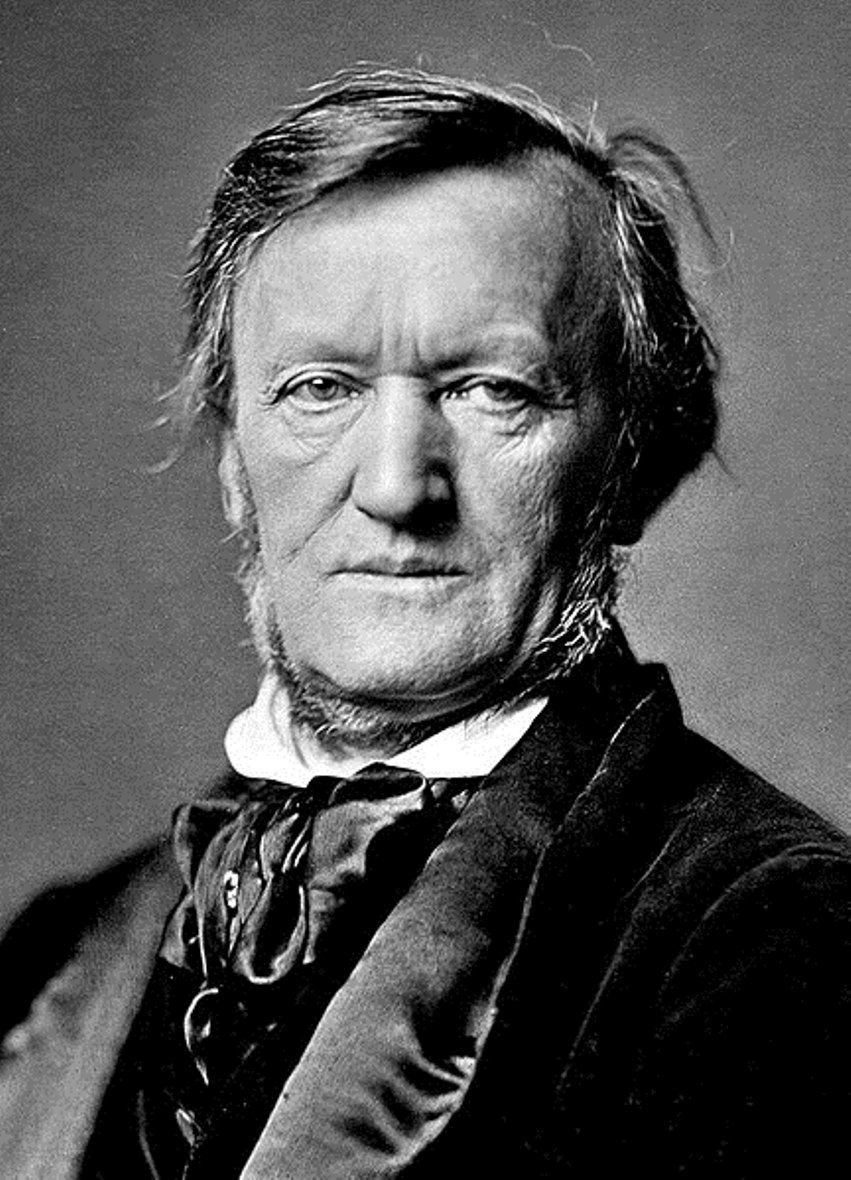
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German pioneering composer, conductor and opera reformer.
His first proper Symphony in C major was performed at the Leipzig Gewandhaus concerts in 1833. Wagner lived in a colony of poor German artists and made his living in music journalism. Nevertheless, in 1841 he wrote his first representative opera, The Flying Dutchman, based on the legend of a ship captain doomed to sail forever. In 1842 his Rienzi was triumphantly performed in Dresden, after which Wagner was appointed conductor of the court opera and held this position until 1849.
In 1848-49 Wagner became involved in the German Revolution, wrote a number of articles in support of it, and took an active part in the Dresden Uprising of 1849. When the uprising failed, he was forced to flee Germany. His subsequent years were occupied mainly with writing theoretical treatises on philosophy and music. Wagner held anti-Semitic and Nazi views. And reflecting on the future of music, he predicted the disappearance of opera as an artificial entertainment for the elite and the emergence of a new kind of musical stage work for the people, expressing the self-realization of free humanity. This new work was later called "musical drama."
By 1857 his style had been enriched with new interpretations, and Wagner had composed "Rheingold," "Die Walküre," and two acts of "Siegfried." By 1864, however, unwise financial habits had driven him into debt and ruin, and he was forced to flee from prison to Stuttgart. He was rescued by King Louis II, an ardent admirer of Wagner's work. Under his patronage for six years in Munich, the composer's operas were successfully staged. The King also practically ensured him a trouble-free life, thanks to his support Wagner built his own opera house (Bayreuther Festspielhaus), in which many new constructive ideas were realized. The premiere of "The Ring" and "Parsifal" took place here.
As a result of all Wagner's creative innovations and methods, a new kind of art emerged, the distinctive feature of which was a deep and complex symbolism, operating in three inseparable planes - dramatic, verbal and musical. He had a significant influence on European musical culture, especially on the development of opera and symphonic genres.
Richard Wagner's major works include The Flying Dutchman (1843), Tannhäuser (1845), Lohengrin (1850), Tristan und Isolde (1865), Parsifal (1882), and his great tetralogy, The Ring of the Nibelung (1869-76).

Richard William Hamilton was a pivotal figure in the evolution of modern art, seamlessly blending traditional mediums with emerging cultural commentary. Born in London in 1922, Hamilton emerged as a leading voice in the pop art movement, a genre that sought to bridge the gap between high art and popular culture. His work, characterized by its innovative use of materials and its critical eye on consumer society, positioned him as a critical link between art's past and its rapidly evolving future.
Hamilton's influence is perhaps best encapsulated in his iconic collage, "Just what is it that makes today's homes so different, so appealing?" Created for the This Is Tomorrow exhibition in 1956, this piece is widely regarded as one of the first works of pop art, predating the more widely recognized contributions of American artists like Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein. By integrating images from magazines, advertisements, and other mass media, Hamilton crafted a visually striking critique of contemporary consumerism and its pervasive impact on the domestic sphere.
Beyond his contributions to pop art, Hamilton's legacy is also preserved in his role as an educator and theorist. His writings and teachings have influenced generations of artists, encouraging them to explore the intersections of art, technology, and society. His works are held in high esteem and are featured in prestigious collections worldwide, including the Tate Gallery in London and the Museum of Modern Art in New York.
For collectors and experts in art and antiques, Hamilton's oeuvre offers a fascinating window into the mid-20th century's cultural shifts. His ability to capture the zeitgeist of his time, while also pushing the boundaries of what art could be, makes his work both historically significant and continually relevant.
To stay informed about new product sales and auction events related to Richard William Hamilton, we invite you to sign up for updates. This subscription ensures you remain at the forefront of the art and antiques world, with a focus on one of its most influential figures.
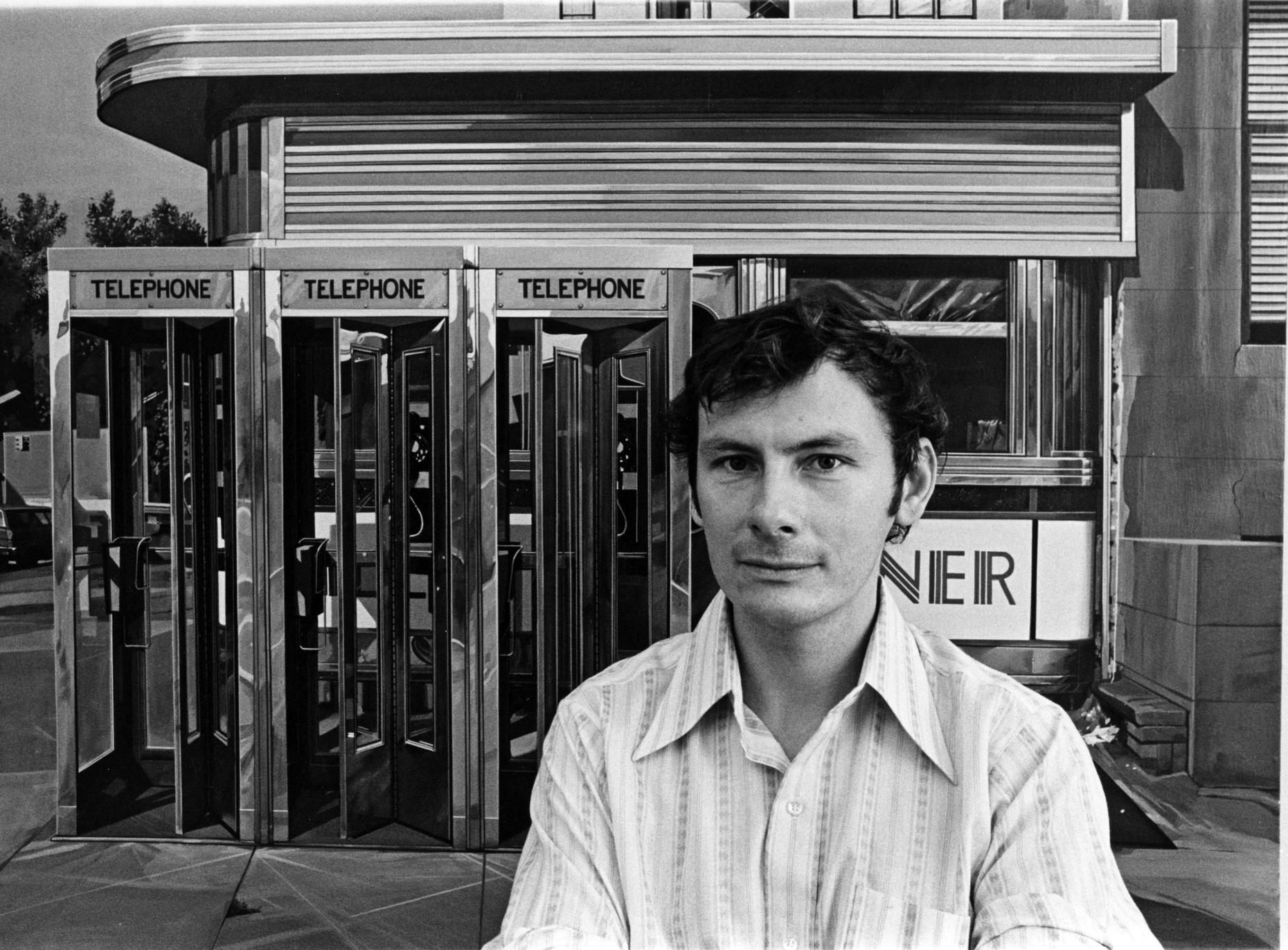


Richard Estes is an American artist, best known for his photorealist paintings. The paintings generally consist of reflective, clean, and inanimate city and geometric landscapes. He is regarded as one of the founders of the international photo-realist movement of the late 1960s, with such painters as John Baeder, Chuck Close, Robert Cottingham, Audrey Flack, Ralph Goings, and Duane Hanson.

.jpg)
Richard Parkes Bonington was an English Romantic landscape painter, who moved to France at the age of 14 and can also be considered as a French artist, and an intermediary bringing aspects of English style to France. Becoming, after his early death, one of the most influential British artists of his time, the facility of his style was inspired by the old masters, yet was entirely modern in its application. His landscapes were mostly of coastal scenes, with a low horizon and large sky, showing a brilliant handling of light and atmosphere. He also painted small historical cabinet paintings in a freely-handled version of the troubadour style.

.jpg)
Richard Parkes Bonington was an English Romantic landscape painter, who moved to France at the age of 14 and can also be considered as a French artist, and an intermediary bringing aspects of English style to France. Becoming, after his early death, one of the most influential British artists of his time, the facility of his style was inspired by the old masters, yet was entirely modern in its application. His landscapes were mostly of coastal scenes, with a low horizon and large sky, showing a brilliant handling of light and atmosphere. He also painted small historical cabinet paintings in a freely-handled version of the troubadour style.















































































